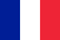
Fungal foot infections start in the areas between the toes. The infection can later spread to the feet and nail bed. The disease is caused by dermatophyte fungi, mold or yeast. According to statistics, in our country about 20% of people have foot fungus. The severity of the disease depends on the type of infection, but in any case the disease must be cured, as peeling, severe itching, inflammation and unpleasant odor in the feet cause great discomfort. We will tell you how to get rid of foot fungus.
What does foot fungus look like?
A fungal infection causes inflammation of the skin where the fungal infection is located. The main types of leg dermatomycosis are:
- The fungus on the sole of the foot is scaly, in which the affected area turns red, peels and cracks appear in the skin. Often the patient does not feel any discomfort, which contributes to the wide spread of this type of disease.
- Dyshidrotic foot fungus is located in the arch of the feet, which is not in contact with the floor surface. At the sites of infection, small blisters form, which spread over the inside and outside of the foot, open, forming erosions and diaper rash on the surface of the skin. The process is accompanied by an itching and burning sensation. After the vesicles (blisters) open, the disease turns into a scaly form.
- A fungus on the skin of the feet that affects the interdigital space is called the intertriginous form of the disease and is the most common type. It appears in the form of cracks, the edges of which are covered with a white border of exfoliating epidermis. As a rule, this form has a long-term chronic course and is difficult to treat.
- Fungus on the shin or ankle appears as round, pink or red patches covered in scales of skin. As the infection progresses, the foci of inflammation increase, the process is accompanied by severe itching.
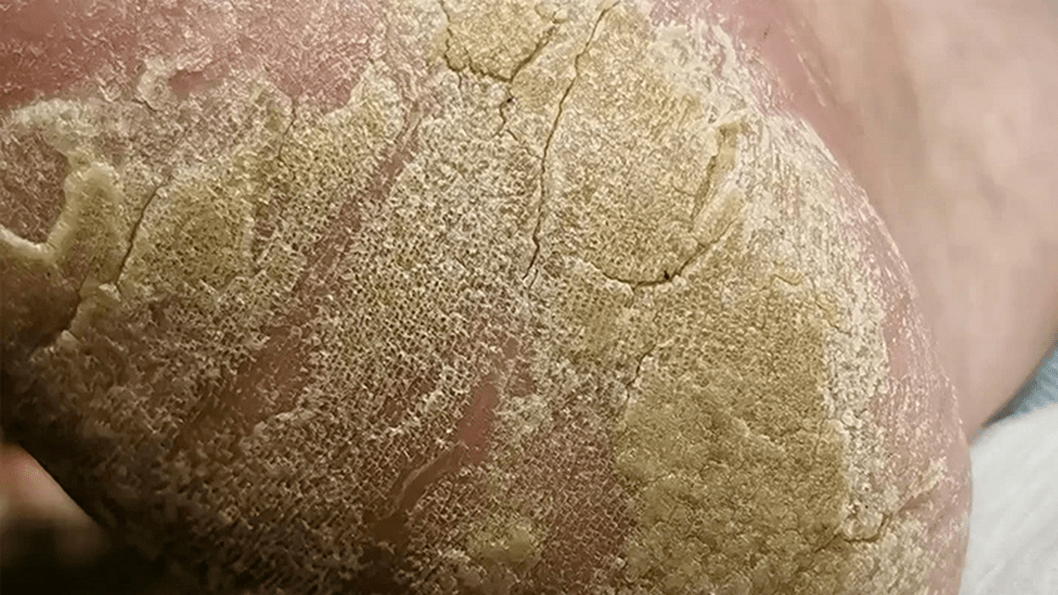

Onychomycosis
This disease is a type of foot fungus characterized by fungal infection of the nails. You can become infected in public showers, saunas, baths and swimming pools. Scales containing a pathogenic microorganism are easily separated from the nail plate and can remain on unpainted floors, carpets, bedding and benches. High humidity allows not only survival, but also promotes active reproduction, and therefore the risk of infection increases significantly.
In the initial phase, the infection affects the epidermis of the feet, causing intense itching. To alleviate the discomfort, the person begins to comb the infected area, but this only makes the situation worse. The areas of the skin affected by the fungus become covered with small scratches and cracks, microorganisms begin to spread, penetrate under the nail plate and then begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Serious illnesses such as diabetes or HIV, poor circulation or nail injuries greatly increase the risk of infection.
Onychomycosis is divided into 3 types:
- Normotrophic. With this type of onychomycosis, a change in nail color from normal to yellowish-brown is observed. The natural shine, shape of the nail and its thickness remain unchanged.
- Hypertrophic. A final change in the color of the nail occurs, its shine disappears, its shape changes, thickening develops and partial destruction begins.
- Onycholytic. The color of the affected nail changes to brown, becomes thinner and begins to break. His gradual separation from the bed begins. Irregular layers may appear on the exposed part of the nail bed.
Treating this type of fungus on the palms and soles with topical medications is ineffective due to the fungus spores being located under the nail. Before starting treatment, the nail must be removed. This is done with the help of keratolytic medications and adhesives are also used. In some cases, it is possible to remove the nail mechanically: the dead parts of the nail are cut off with a file or tweezers. It is important to remember that all instruments used must be sterile.
The combined use of mechanical removal and keratolytic adhesives is the most effective way to remove diseased nails. As for keratolytics, you can use a ready-made kit with a broad-spectrum antifungal. It contains a special ointment, nail files and an adhesive. After removing the nail plate, you should start taking systemic antifungals: an antifungal for systemic use, an oral antifungal.
Symptoms
Depending on the form of the disease and the location of the inflammation, the infection is accompanied by different symptoms with several of the following general signs:
- peeling of the skin;
- mild or intense redness of the skin at the site of the injury;
- itch;
- burning sensation;
- rashes with blisters or cracks in the skin.
Blisters between the toes
The main symptom of athlete's foot, caused by the Candida fungus, is the appearance of blisters between the toes, usually between the fourth toe and the little toe. The course of the disease is accompanied by swelling of the skin adjacent to the fingers, pronounced areas of redness with small blisters on the surface. The source of inflammation is surrounded by a border of exfoliated epidermis.
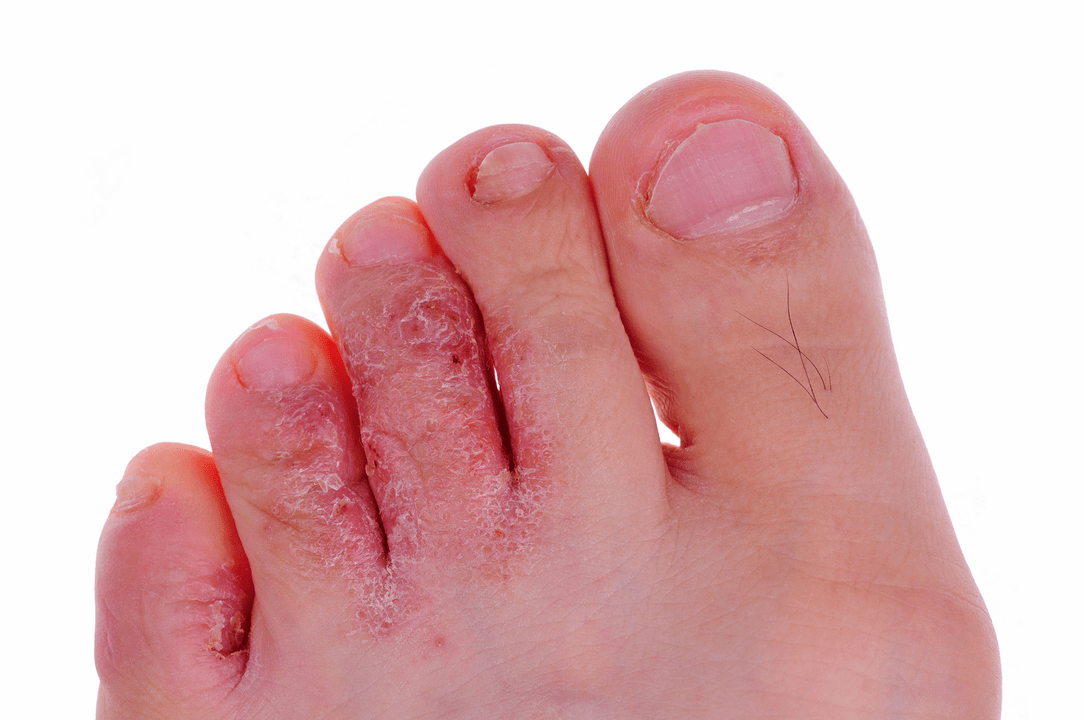
dihydratic form
Vesicular fungus, or, as it is also called, dyshydratic mycosis, is the rarest type of disease. Its main manifestation is numerous vesicles united in conglomerates. Vesicles are blisters filled with pus or nutrient fluid inside. When the liquid begins to turn cloudy, the vesicles rupture, leaving ulcers in their place. They begin to merge into one line, forming pronounced scars on the skin. This occurs due to dryness and peeling of the skin layers.
About 70% of vesicular fungal infections are accompanied by allergic skin rashes. A variety of bacteria and viruses begin to penetrate the ulcers. As a result, the disease becomes mixed and identification of the original pathogen becomes more difficult. Therefore, you should consult a doctor as soon as the primary symptoms appear: he will be able to quickly identify the type of foot fungus and begin therapy.
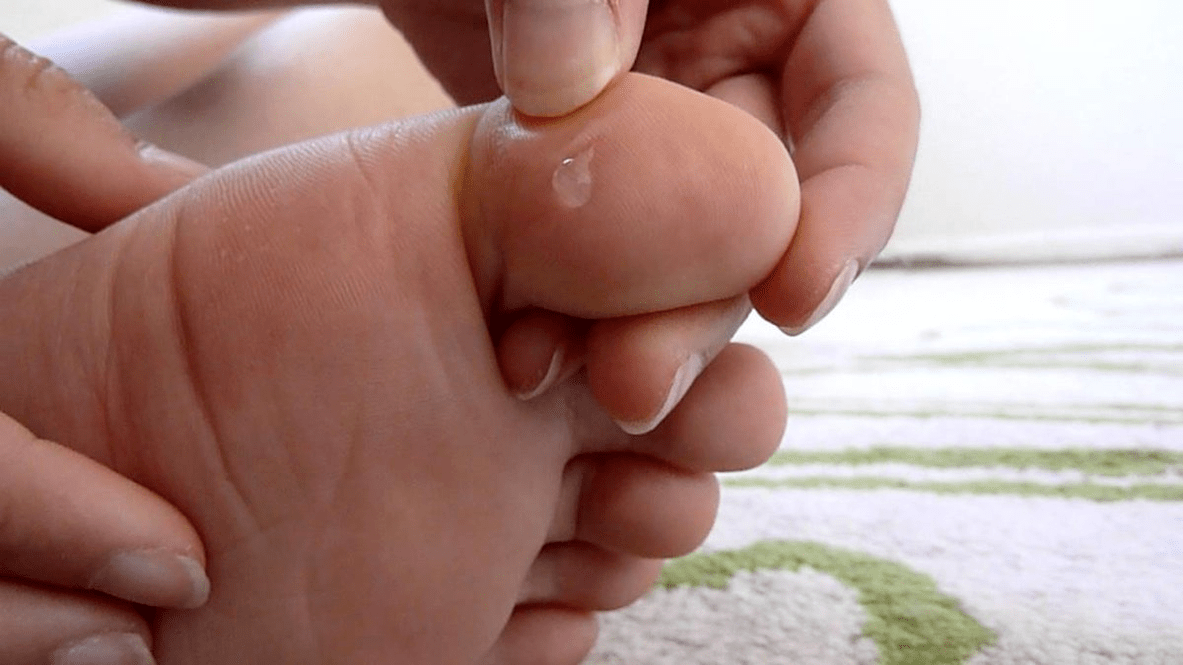
Furthermore, this must be done immediately. First of all, before using antimycotics, the acute process must be eliminated. It is best to entrust this task to a specialist: he can carefully pierce the vesicles, treat the remaining ulcers with 2% boric acid and apply a brilliant green or methylene blue solution.
Treatment of advanced disease involves the use of corticosteroid ointments. After eliminating the inflammatory process, it is recommended to use topical antimycotics. This will suppress the pathogen. We continue to consider the names and types of foot fungus.
First signs
Skin disease on the legs is always accompanied by a number of general symptoms, the appearance of which indicates skin infection with spores of harmful microorganisms. You should seek help from a dermatologist in the following cases:
- the appearance of cracks or blisters in the skin in the folds of the feet or between the toes;
- significant thickening and thickening of the skin of the feet;
- redness of areas of the skin, peeling;
- burning or itching sensation.
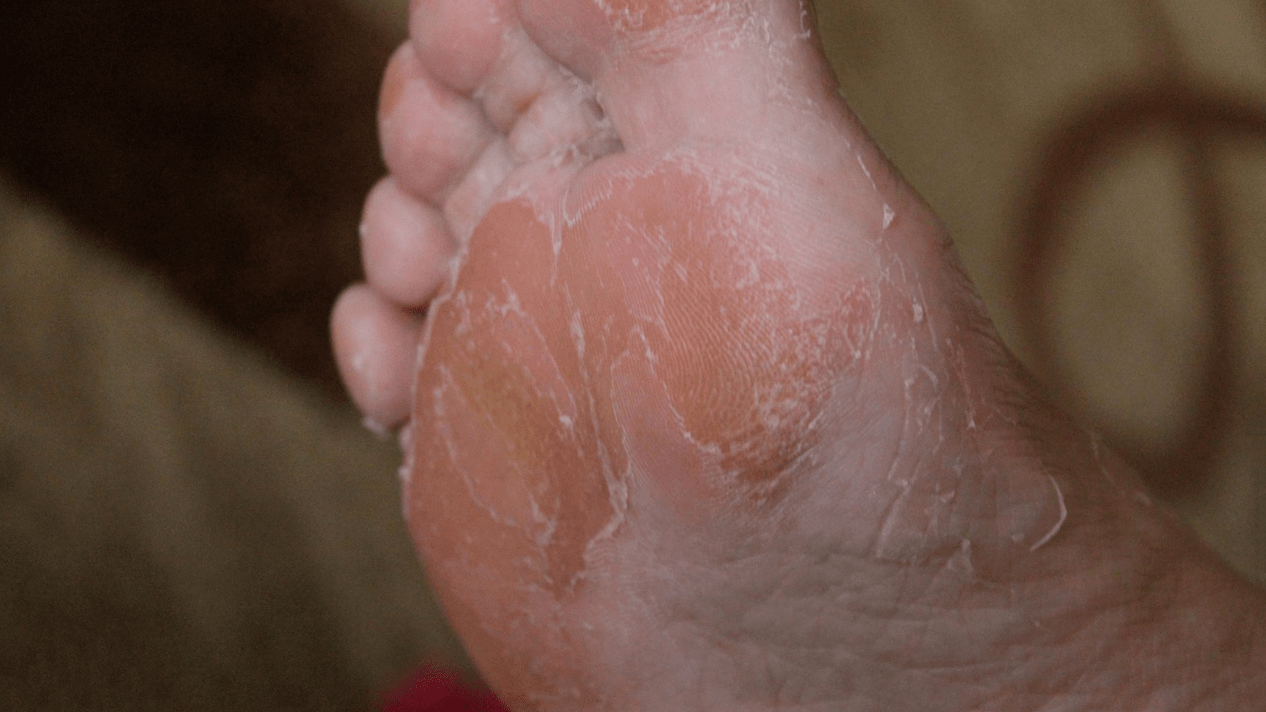
Duration of treatment
Combined infection of the skin and nail plate requires rehabilitation therapy for one to three months. These terms are considered standard for the most medically effective pharmaceutical products.

Pregnancy requires a charming visit to the doctor to choose a way to get rid of mycodine infection. Potent medicines and therapies that require the use of similar medicines are prescribed only under the supervision of a doctor in compliance with strict dosages. Many antibacterial tablets that effectively destroy fungi can cause visible harm to the fetus. Therefore, whenever possible, during pregnancy, it is recommended that patients be treated with traditional medicine recipes. Many of them allow you to cope with the disease, but provided that the disease has not reached a complex stage. Only classical medicine can help deal with the advanced form.
Modern medicines allow you to completely restore leg health in two weeks, provided that signs of infection are detected in time.
Causes
Infection occurs for various reasons after direct or indirect contact of the patient with the carrier of the infection or his personal belongings, household items. Risk factors for getting tinea pedis include:
- circulatory disorders in the legs and related diseases (varicose veins);
- weakened general or local immunity;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- weakening of the body's defense systems after taking antibiotics;
- increased sweating of the skin of the feet;
- presence of minor damage to the skin (abrasions, scratches).
Treatment methods
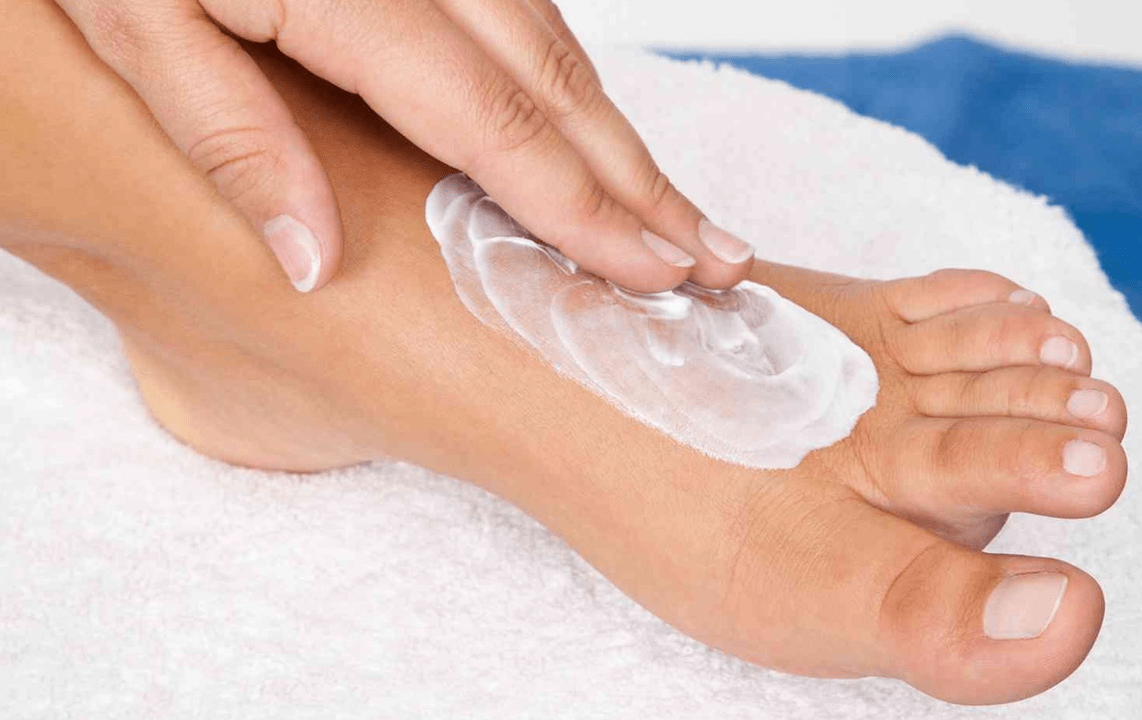
In most cases, it is possible to completely get rid of a detected disease in time, within a month at most. This is a very important point in treatment, as itching, tissue damage and other manifestations disappear, the patient sometimes stops treatment, believing that the disease has been defeated. But the remnants of the infection can easily trigger a relapse.
Treatment procedures should be stopped only after authorization from the doctor and after passing the necessary tests. This is especially true for advanced forms of the disease. The fungus is firmly "fixed" in the body and can sometimes take at least six months to get rid of it. But the external manifestation of foot fungus in the form of various damage to the skin or nails disappears much earlier, creating the illusion of health. By stopping therapy in this case, the patient is almost certain to relapse.
Foot treatment for mycoid infection is carried out comprehensively. To get rid of the disease, local antifungal drugs and tablets are used to eliminate the infectious agent that has penetrated the body. To eliminate itching, pain, brittle nails and accelerate tissue regeneration, certain medications may be prescribed. It is not recommended to combine them independently with the main therapeutic group, so as not to provoke an allergic reaction or intoxication of the body due to the simultaneous use of incompatible medications.
Curing foot fungus at an early stage is quite simple. Typically, two weeks of therapy are enough to eliminate the symptoms of mycoid infection.
Types of mycoses
Only a dermatologist can accurately determine the type of fungus through a visual examination, the data of which is clarified through laboratory tests. Depending on the causative agent of the fungal infection (yeast, mold, fungi of the genus Trichophyton or Candida) on the skin of the feet, there are several main types of the disease, which include:
- candidiasis of the feet;
- athlete's foot;
- trichophytosis (or rubicosis) of the feet;
- onychomycosis (nail fungus).
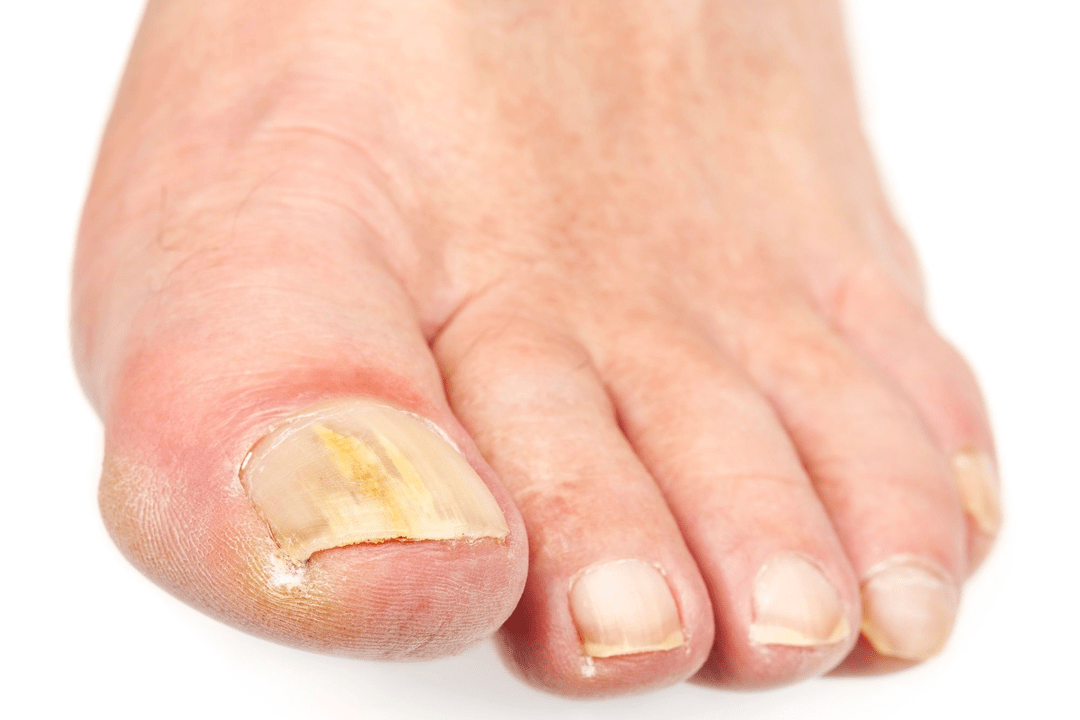
Prevention
Simple preventive measures will significantly reduce the likelihood of infection. You should only use personal belongings and treat your nails with sterilized instruments. When visiting public places, such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, beaches, you must wear appropriate footwear. In fact, try to choose it so that it is comfortable and allows your feet to breathe. You should worry about prevention in advance so you don't have to deal with various types of foot fungus later.
How to treat
Treatment of fungus on the skin of the legs is a long-term complex therapy, in severe cases including the use of systemic oral agents. For smaller lesions, the emphasis is on local therapy with antibacterial and antiseptic agents. In acute forms of the disease, hot baths are prescribed to relieve inflammation and remove dead skin cells. In some cases, it is necessary to treat the patient's shoes and clothes with special compounds to prevent relapses.
System Tools
Systemic oral agents are prescribed in cases where local medications are ineffective and in severe and advanced forms of the disease. A course of oral antifungals is indicated for fungal infections of the deep layers of the skin, as they help not only to treat the acute phase, but also to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. The dosage regimen, course duration and dosage are selected by the attending physician.
Doctors recognize antifungal drugs for systemic use as the best means for systemic treatment of foot fungus. They have an active fungicidal (destroying) and funginic (suppressing the proliferation of bacteria) effect, their active components can accumulate in the upper layers of the epidermis, nails and hair. Before taking it, read the instructions for use, as these products have contraindications.
Local remedies
Topical drug therapy includes not only the use of antifungal creams and ointments, but also the use of special sprays, aerosols and lotions. The form of the drug is recommended by a dermatologist depending on the type of agent causing the infection, the severity of the lesion on the skin of the legs, the stage of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient's body. The duration of treatment with local medication can vary from 2 weeks to 3 months.
For foot fungus and other forms of mycoses of the skin of the legs, an aerosol, a suspension for application to the skin, or a solution for topical use may be prescribed. The products are applied directly to the skin damaged by the fungus or damp cotton swabs soaked in a medicinal solution are applied. All necessary recommendations for use can be obtained from your doctor.
Antifungal ointments
When treating fungus on the skin of the feet, in most cases an antifungal ointment is prescribed, for example, a cream with the active ingredient terbinafine hydrochloride or its analogues. Apply the medicine in the form of an ointment or cream to the dry skin of the heels or other areas where inflammation is located, previously carefully cleaned of dead epidermal cells and any other plaque. For different types of diseases, the duration of treatment can vary from 2-3 weeks to 2-3 months.
Experts consider broad-spectrum ointments to be an effective means of combating foot fungus in various forms and stages. The active components of the drug locally fight the fungal infection, suppressing the reproduction of its pathogen. The ointment is applied two to three times a day to washed affected skin for several weeks or months, depending on the degree of skin damage.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is possible only with the consent of the attending physician. The main products for baths, compresses and applications against fungus on the skin of the feet are vinegar, propolis, sodium bicarbonate, decoctions of medicinal plants and washing powder. The following procedures are practiced:
- Baths with soda and salt solution. For 3 liters of water at a temperature of 36-40°C, use 3 tbsp. I. salt and 3 tbsp. l soda. The duration of the procedure is 10 to 15 minutes, after showering, rinse your feet under warm running water. Used for acute forms of fungus for 7-10 days twice a day.
- Lotions with herbal decoction. To prepare a decoction, mix dry oak bark, calendula flowers and verbena leaves in equal proportions. To prepare the decoction 3 tbsp. I. Pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and keep on low heat for 10-15 minutes. Make a compress from the resulting decoction three times a day for 20-30 minutes.
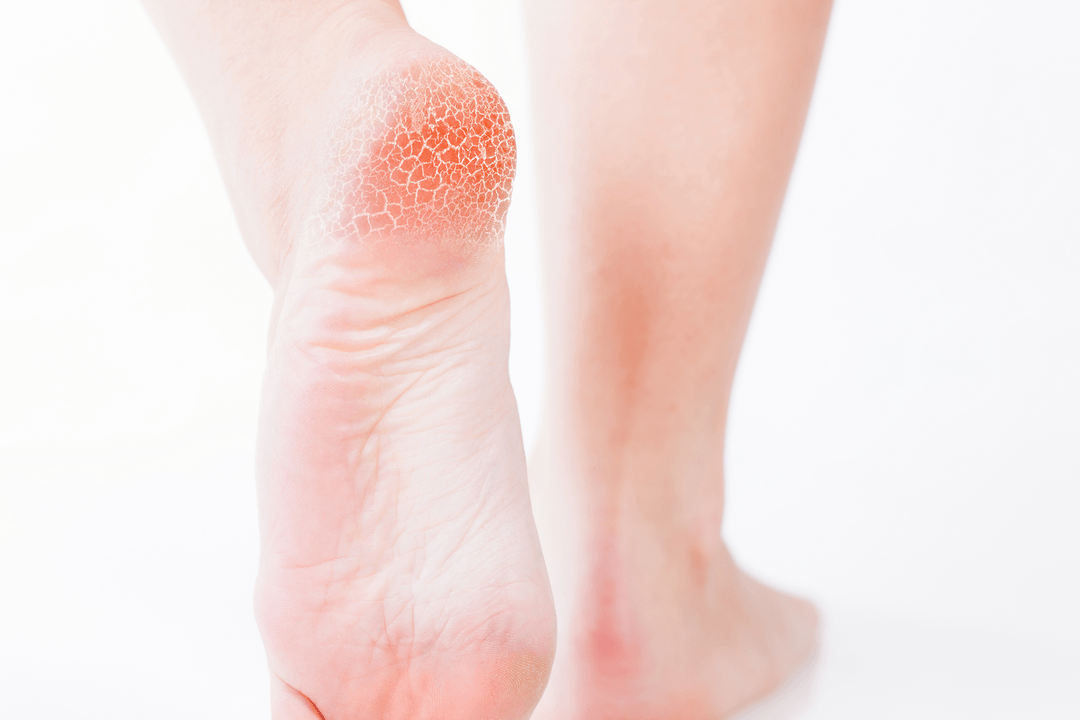
Form deleted
Mycosis of the erased form is almost invisible, its symptoms are minimal. These include: mild itching, burning, flour-like peeling, microcracks located in the interdigital areas. If you do not seek a specialist when the first signs of the disease appear, the pathology can evolve into the form of onychomycosis, which is much more difficult to treat. In this case, the peeled nail will grow back in one to six months.
Erased mycosis is treated with local preparations: ointments, creams, foams. They allow you to create a layer on the foot that will protect against infection by other infections. It is not recommended to wash your feet for 24 hours after applying this medicine.
Only in extreme cases can systemic therapy be prescribed. The problem is that these drugs are toxic and negatively affect some internal organs, such as the liver. Therefore, if there is an effect from using local remedies, it is better not to take pills.
Infection routes
Fungal spores remain viable in the environment for a long time, so it is easy to become infected with the disease in the most unexpected places. But the most favorable conditions for its development are heat and high humidity. Because of this, people who visit the following are at risk:
- pools;
- baths;
- saunas;
- fitness centers;
- beaches.
The fungus can appear on anything located there, even if regular disinfection is carried out. Therefore, in these places you should avoid common objects and take spare shoes with you.
The military is at risk. Most of the time, army soldiers wear uncomfortable shoes that do not allow air to pass through. Because of this, the feet sweat, microtraumas appear, into which the fungus penetrates.
There are two types of infection. The first is the direct route through direct contact with the infectious agent when communicating with a sick person, caring for an animal or walking barefoot on the ground and sand. The second - the indirect route leads to infection through objects belonging to infected people or pets.
Preventive measures

Preventing a disease is always easier and safer for your health than treating it, even with the most gentle method. In the case of a fungal infection, prevention is one of the mandatory rules of life, as it is very easy to become infected. Therefore, to reduce the risk of contracting the disease, it is recommended to follow some simple rules:
- try to eat healthily and as healthily as possible;
- do not use other people's things and personal hygiene products;
- use basic protective equipment in public places, such as spare shoes and hygienic antibacterial agents;
- wash your feet and change socks regularly;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Take regular baths to improve foot health;
- periodically disinfect your shoes.
Preventing fungal infection is important not only to prevent it, but also if the disease occurs. In this situation, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards helps to accelerate healing and prevent infection of others with the fungus.